3D PRINTING WITH FLASHFORGE FINDER
- Introduction to 3D Printing
https://core-electronics.com.au/tutorials/3d-printing-and-modelling-workshop.html
Download Flashprint Slicer Program
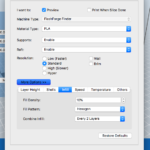
Operation:
- Level Build plate(if needed)
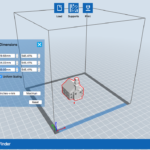
- Open STL file(from SketchUp) with Flashprint
- Within Flashprint say OK to Repair and Place Model on Build Plate
- Scale Model to size
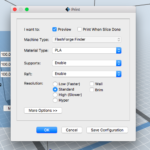
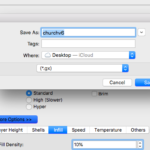
- Hit "Print"- select infill and raft settings as needed
- Move Gcode file (.gx) to USB drive
- Insert USB Drive into printer
- On printer display screen, select model file on USB drive and click print.
Terminology
When stepping in the world of 3D printing you will encounter several technical terms. Below you can find a glossary of the most common 3D printing terms.
Fused filament fabrication (FFF)
An additive manufacturing technology that is based on the principle of laying down material in layers. This is the 3D printing technique that Ultimaker uses.
Filament
The material that is used for 3D printing. It has the shape of a wire and is usually coiled on a spool.
PLA
This is a hard, odorless bioplastic that has a low environmental impact. It is derived from renewable, starch-based resources. PLA has a very low shrinkage, which is ideal for 3D models and prototyping at home.
ABS
This plastic is well-known for its strength and industrial purposes. ABS is impact resistant, very hard, whilst retaining good flexibility. Compared to PLA, ABS has a high shrinkage, which means that it’s harder to print with this material.
Layer resolution
The layer resolution (or layer height) describes the thickness of one layer of the 3D print. With an Ultimaker the default layer resolution is 0.1 mm (100 micron), but it can even reach a 0.02 mm (20 micron) layer height. You will however need quite some 3D printing experience for this.
Raft
A flat initial layer laid down as the base of a 3D print, which helps the model adhere to the build plate.
Supports
Additional temporary pieces added to a model, to support overhanging design elements during printing
Infill
The ratio of plastic to air in interior parts of the model, often set to 10% or less to improve printing speed.
Positioning precision
The accuracy with which the print head moves around in the X and Y direction. Instead of moving around in a perfect cirle it moves around in steps of 12.5 micron.
Print speed
The speed at which the print head moves while it is printing. Based on the print speed the amount of plastic that needs to be extruded will be calculated.
Travel speed
The speed at which the print head moves while it is not extruding any plastic.
Firmware
The software that runs on the electronics and controls the Ultimaker.
STL
A widely used file format for 3D models. This is one of the file formats accepted by our software Cura.
Slicing
The process of converting a 3D model into a printable file. It will divide the model into “slices” so that the Ultimaker can build it up layer by layer.
G-code
The file format that is used for 3D print files (after it has been sliced). A G-code file basically exists of coordinates that control the movements of the Ultimaker.
Extruder
A common name for the parts that control the extrusion of the filament. This means that the extruder on an Ultimaker exists of the material feeder, bowden tube and print head.

- Session 1: Introduction to Sketching
- Session 2: Introduction to SketchUp- Tutorials 1&2
- Session3: SketchUp Tutorials #3 and #4
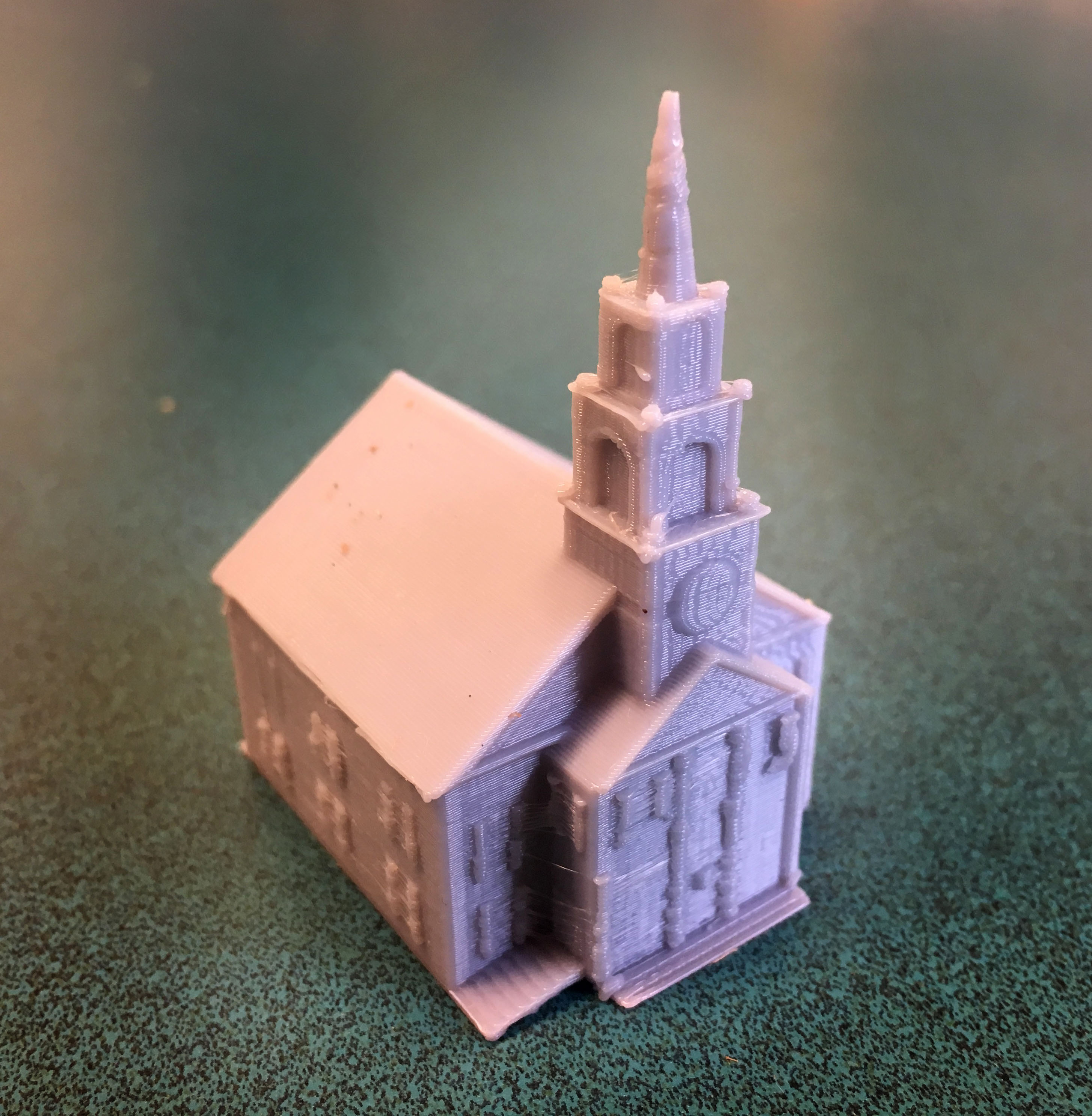
- Session 4: Measurements of the First Church
- Session 5: Drawing the First Church in SketchUp( or other object or building)
- Session 6: 3D Printing-Using Flashprint to adjust, scale, and print 3D models